White corn gives Cagayan farmers a lifeline after years of debt and flood losses
By Vonn Andrei E. Villamiel
CAGAYAN — For decades, Crecencia B. Garan planted yellow corn in the river plains of Alcala, Cagayan — only to watch most of her earnings circle back to the middlemen who financed her inputs.
Each planting season left the 67-year-old Filipino deeper in debt, and each flood that swept through her low-lying community wiped out whatever gains remained.
“For yellow corn, we shoulder all the expenses, and we often borrow from middlemen,” she told reporters invited by the Agriculture department to Alcala on Dec. 5 in Filipino. “What we earn just ends up being used to pay our debts.”
 Today, Ms. Garan says she is finally making money from the same land. She is part of a small but rising group of farmers shifting to white corn, a variety long grown for household consumption but now fetching higher prices and attracting steadier buyers as Alcala tries to rewire its corn economy.
Today, Ms. Garan says she is finally making money from the same land. She is part of a small but rising group of farmers shifting to white corn, a variety long grown for household consumption but now fetching higher prices and attracting steadier buyers as Alcala tries to rewire its corn economy.
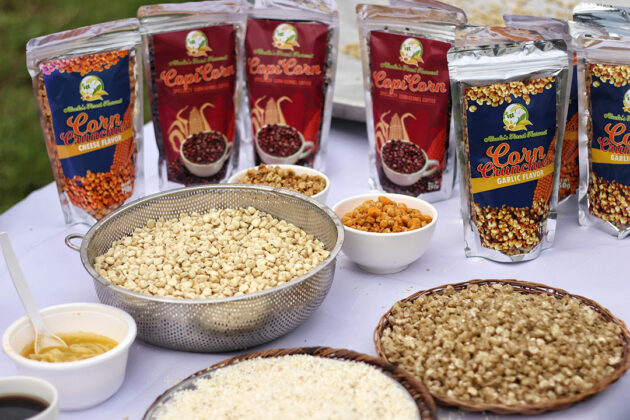
While yellow corn is a feed and industrial crop, white corn is eaten directly and draws higher farmgate prices — P35 to P45 per kilo, roughly double the P18 farmers usually get for yellow corn.
Grown alongside the yellow variety, white corn has become a crucial second stream of income that helps farmers absorb losses from the more volatile yellow corn market.
Input access has also changed the equation. Seeds, fertilizer and pesticides are provided by government programs pushing white corn planting, while Alcala’s municipal processing hub buys the harvest and channels it to institutional buyers.
“Because of white corn, we earn more because of higher prices,” Ms. Garan said. “Farmers also receive free fertilizer and insecticide, and we can borrow tractors and rotavators.”
Alcala’s farmers have long depended on yellow corn, grown across more than 4,200 hectares and sold to livestock growers and feed millers across Cagayan Valley.
That model began to crack after Typhoon Ulysses struck in 2020, sending floodwaters across the province and destroying about P52 million worth of crops and livestock in Alcala alone.
Municipal agriculturist Vincent C. Espejo said years of heavy herbicide use in yellow corn areas contributed to vegetation loss and soil runoff, worsening the impact of flooding.
Local officials began looking for crops that required fewer chemicals and encouraged more manual weeding — conditions that pointed them to white corn.
“We have about 4,200 hectares planted to yellow corn, and almost all of them use herbicide,” Mr. Espejo said in Filipino. “The local government decided to adopt white corn because it does not use herbicide.”
Today, about 100 hectares in Alcala are planted with white corn, producing roughly 170 metric tons per cycle.
The changes required deliberate intervention. During the first harvests, the town government had to buy white corn because there were no buyers yet.
“We bought it at P25 per kilo and sold it at P20 per kilo,” Mr. Espejo said. “The LGU (local government unit) would incur losses, and that was not sustainable.”
That experience led to the creation of the Alcala Product Center, which now buys white corn, processes part of it, and connects farmers to institutional buyers.
One of them is snack maker Nacho King, which buys at P45 per kilo and has a monthly requirement of up to 10 metric tons, according to Alcala’s agriculture office.
‘BIG BROTHER’
The center’s purchases reach about 30 metric tons per cropping cycle. Roughly 3 tons are turned into corn-based products — noodles, coffee, corn bits and corn rice — sold in groceries, trade fairs and pasalubong stores, reaching markets as far as Manila and Palawan.
The Alcala Fine Producers Cooperative, which manages the center, uses what it calls a “big-brother, small-brother” setup to support growers.
“We are the big brother, and they are the small brother,” cooperative manager Jennifer M. Pagaduan told reporters in Filipino. “We help them process and market their products. They no longer need to find buyers themselves.”
For farmers like Belly A. Duruin, president of the White Corn Growers Association, the mix of input assistance, equipment access and market guarantees has transformed their outlook.
“This is a big help to us farmers,” she said in Filipino. “Because of growing white corn, our income increased. We no longer suffer losses.”
Still, expansion remains slow. Of Alcala’s more than 4,000 hectares of corn land, only around 100 hectares have shifted to white corn. Habits, market familiarity, and yield differences continue to anchor farmers to yellow corn.
“White corn is more labor intensive,” Mr. Espejo separately told BusinessWorld. “Unlike yellow corn, which only needs to be sprayed with herbicide, white corn requires manual weeding.”
White corn yields about 2 metric tons per hectare, less than half the 5 tons typical for yellow corn. And although white corn commands higher prices, its market is smaller. Yellow corn remains easier to sell — traders and livestock growers will pick it up directly from farms.
The processing center has also reached its limits. Drying equipment is scarce, and the town still lacks a proper warehouse for bigger volumes.
Despite the constraints, Alcala sees momentum turning. As more buyers explore white corn for snacks and other food products, farmers are finding demand that did not exist just a few years ago.
“When demand for white corn increases, production will also increase. Before, buyers could only find yellow corn, but now producers are available,” Mr. Espejo said.
The local government aims to expand white corn planting to 20% of Alcala’s corn land — around 800 hectares — within five years.
The expectation is that demand for locally grown white corn will continue rising as processors and food manufacturers search for unique ingredients and as consumers explore alternatives to traditional staples.
For now, farmers like Ms. Garan say white corn has already changed their lives. After decades of borrowing from middlemen, she says she no longer ends each harvest season in debt.
“We no longer suffer losses. We earn more now.”